Study shows Magazines are the medium of engagement
-
From the 2011/12 Magazine Media Factbook, published by the The Association
of Magazine Media, Magazines are the *medium of engagement*. "Magazines
continu...
Peanuts: The Cure for Peanut Allergies
 12-million Americans suffer from food allergies. More than three-million of them are allergic to peanuts. While there are drugs to treat an allergic reaction, there's nothing that can fix food allergies for good. Now, doctors are using peanuts themselves to treat allergies. The goal is to cure the potentially life-threatening condition.
12-million Americans suffer from food allergies. More than three-million of them are allergic to peanuts. While there are drugs to treat an allergic reaction, there's nothing that can fix food allergies for good. Now, doctors are using peanuts themselves to treat allergies. The goal is to cure the potentially life-threatening condition.The new treatment mixes a tiny amount of peanut powder -- about one-thousandth of a peanut -- into a child's food. Gradually, they increase the dose over time.
"We see the first changes to the immune system happen about six months into treatment and then further changes happen beyond a couple years of the treatment," Wesley Burks, M.D., Professor of Pediatrics at Duke University Medical Center.
In the four-year study, 89-percent of the kids with severe peanut allergies could eat up to 15 peanuts. 12 percent had to drop out because they couldn't handle the treatment, but another 25 percent lost their peanut allergies altogether in another part of the study.
Doctor Burks says this was a medically-supervised study, and parents should not try the approach at home. Doctors at Duke University and Arkansas children's hospital are still enrolling kids in more peanut allergy studies. They believe there will be a treatment for peanut allergies in the next two or three years.
Cancer Detecting Mouthwash
 For a patient with head and neck cancer, the cure rate is only 30 percent. That's because the disease is often detected in the late stages. Now catching the cancer earlier may be as simple as gargling and spitting in a cup. A new mouthwash may be able to see what doctors can't.
For a patient with head and neck cancer, the cure rate is only 30 percent. That's because the disease is often detected in the late stages. Now catching the cancer earlier may be as simple as gargling and spitting in a cup. A new mouthwash may be able to see what doctors can't.For patients, late stage diagnosis makes treating neck cancer more difficult. Researchers developed a quick, inexpensive mouthwash to detect head and neck cancers earlier.
The patient rinses with the saline mouthwash. After they spit it out, doctors add antibodies that identify molecules involved with cancer. In about 48 hours, if there's cancer detected in the saliva, the molecules show up in color.
"We've found that these molecules show up differently in the oral rinses from patients that have cancer compared to patients that don't have cancer," Elizabeth Franzmann, M.D., an otolaryngologist at Sylvester Cancer Center at the University of Miami.
In a study that included 102 head and neck cancer patients and 69 patients with benign disease, the oral rinse distinguished cancer from benign disease nearly 90 percent of the time.
If head and neck cancer is caught early, doctors say they could be able to cure at least 80 percent of cases. They're working on a version of the mouthwash that can be used as an over-the-counter test or administered at community health centers.
Understanding Down Syndrome

What Is Down Syndrome?
Down Syndrome is one of the most common birth defects. Usually, children born with the condition have some degree of mental retardation, as well as characteristic physical features. Many of these children also have other health problems.
Each year in the United States, approximately one in every 800 to 1,000 newborns has Down syndrome. This translates to approximately 5,000 children. In the United States today, Down syndrome affects approximately 350,000 people. As many as 80% of adults with this condition reach age 55, and many live longer.
The most common form of Down syndrome is often called " trisomy 21" because individuals with this condition have three copies of the 21st chromosome.
What Causes It?
Normally, each cell in the human body contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, which contain the genetic material that determines all our inherited characteristics. We receive half of each chromosome pair from our mother and the other half from our father. Individuals with the most common form of Down syndrome, trisomy 21, have an extra 21st chromosome.
No one knows exactly why this chromosomal error occurs, but it does appear to be related to the age of the mother. At age 25, a woman has a one in 1,250 risk for having a child with Down syndrome. The risk increases to one in 952 at age 30, to one in 378 at age 35, to one in 106 at age 40 and one in 35 at age 45. However, 80% of children born with Down syndrome are born to mothers under the age of 35. This is because most babies, in general, are born to younger women.
Down Syndrome is one of the most common birth defects. Usually, children born with the condition have some degree of mental retardation, as well as characteristic physical features. Many of these children also have other health problems.
Each year in the United States, approximately one in every 800 to 1,000 newborns has Down syndrome. This translates to approximately 5,000 children. In the United States today, Down syndrome affects approximately 350,000 people. As many as 80% of adults with this condition reach age 55, and many live longer.
The most common form of Down syndrome is often called " trisomy 21" because individuals with this condition have three copies of the 21st chromosome.
What Causes It?
Normally, each cell in the human body contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, which contain the genetic material that determines all our inherited characteristics. We receive half of each chromosome pair from our mother and the other half from our father. Individuals with the most common form of Down syndrome, trisomy 21, have an extra 21st chromosome.
No one knows exactly why this chromosomal error occurs, but it does appear to be related to the age of the mother. At age 25, a woman has a one in 1,250 risk for having a child with Down syndrome. The risk increases to one in 952 at age 30, to one in 378 at age 35, to one in 106 at age 40 and one in 35 at age 45. However, 80% of children born with Down syndrome are born to mothers under the age of 35. This is because most babies, in general, are born to younger women.
Too Much Exercise May Pose Arthritis Risk
 Weekend warriors, take note: Too much exercise may place you at risk for arthritis.
Weekend warriors, take note: Too much exercise may place you at risk for arthritis.A new study shows that middle-aged men and women who engage in high levels of physical activity -- at home and at work as well as at the gym -- may be unwittingly damaging their knees and increasing their risk for osteoarthritis.
The study involved men and women of healthy weight, without pain or other symptoms. Knee injuries were more common and more severe among those who engaged in the highest levels of physical activity, says Christoph Stehling, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, and the University of Muenster, in Germany.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
High-Impact Exercises Worse for Knee Health
Doctors aren't sure that painless cartilage and bone damage can lead to osteoarthritis, but they think they do, says RSNA spokesman Joseph Tashjian, MD, president of St. Paul Radiology, in Minnesota.
What is known, he tells WebMD, is that high-impact, weight-bearing activities such as running and jumping are worse for knee health and carry a greater risk of injury over time.
"Conversely, low-impact activities, such as swimming and cycling, may protect diseased cartilage and prevent healthy cartilage from developing disease," Stehling says.
Osteoarthritis, in which the wear and tear of joints over the years leads to the breakdown of cartilage, affects about 27 million Americans, according to the CDC.
More Activity, More Knee Damage
The study involved 136 women and 100 men, ages 45 to 55, within a healthy weight range. The participants were separated into low-, middle-, and high-activity groups based on their level of physical activities, which included everything from running to yard work and washing the kitchen floor.
"A person whose activity level is classified as high typically might engage in several hours of walking, sports or other types of exercise per week, as well as yard work and other household chores," Stehling says.
The researchers took MRI scans of study participants' knees, looking for signs of bone, joint and cartilage damage.
Results showed that people in the high-activity group had much more damage, including cartilage and ligament lesions and buildup of fluid in the bone marrow, than those in the low-activity group.
For example, 93% of people in the high-activity groups suffered cartilage damage vs. 60% in the low-activity group. And cartilage damage was three times more severe in the high-activity group.
The participants' age or sex didn't affect their risk of knee injury, Stehling says.
The researchers are continuing to follow the participants to see if those in the high-activity group actually develop arthritis and if low-impact vs. high-impact activities affect their risk.
Researchers Say CT Scan Images Sent via iPhone Clear Enough for Appendicitis Diagnosis
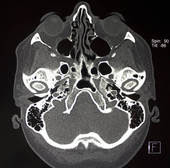 CT Scan images sent via an iPhone, using a $19.99 app that's available on iTunes, were clear enough for correct diagnoses to be made in 99% of cases, researchers say.
CT Scan images sent via an iPhone, using a $19.99 app that's available on iTunes, were clear enough for correct diagnoses to be made in 99% of cases, researchers say.Yes, There is an app for it!
In fact, almost any smart phone will do, says Elliot Fishman, MD, director of diagnostic imaging and body CT at Johns Hopkins University.
"The promise is that we can look at anything anywhere" says Fishman, who is familiar with but not involved in the research.
The technology can expedite diagnosis and, therefore, treatment, he tells WebMD.
CT Scan Images Sent on Smart Phone
For the study, researchers took CT images of 25 patients suspected of having appendicitis and sent them via iPhone to five radiology residents. Then, the residents were asked to make a diagnosis based on what they could see on their phones.
Only one reader failed to make the right diagnosis.
In every other case, the residents correctly determined that 15 of the patients were suffering from appendicitis and that 10 of the patients did not have appendicitis and did not require treatment.
Asim Choudhri, MD, a fellow in neuroradiology at Johns Hopkins who performed the study while at the University of Virginia in Charlottesville, presented the findings here at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Smart Phone Not for Final Diagnosis
Choudhri tells WebMD that a detailed image can be sent in one to five minutes on a smart phone depending on the type of connection that's being used.
Joseph Tashjian, MD, president of St. Paul Radiology and a spokesman for RSNA, says that the application might also be useful for patients who want to bring their medical records along when visiting another facility.
But the application, which is not approved by the FDA, should not be used to make a final diagnosis, he tells WebMD.
"It's a distribution method that can facilitate decision-making," Tashjian says.
"Transmitting the images over a mobile device allows for instant consultation and diagnosis from a remote location. It can also aid in surgical planning," he says.
In fact, almost any smart phone will do, says Elliot Fishman, MD, director of diagnostic imaging and body CT at Johns Hopkins University.
"The promise is that we can look at anything anywhere" says Fishman, who is familiar with but not involved in the research.
The technology can expedite diagnosis and, therefore, treatment, he tells WebMD.
CT Scan Images Sent on Smart Phone
For the study, researchers took CT images of 25 patients suspected of having appendicitis and sent them via iPhone to five radiology residents. Then, the residents were asked to make a diagnosis based on what they could see on their phones.
Only one reader failed to make the right diagnosis.
In every other case, the residents correctly determined that 15 of the patients were suffering from appendicitis and that 10 of the patients did not have appendicitis and did not require treatment.
Asim Choudhri, MD, a fellow in neuroradiology at Johns Hopkins who performed the study while at the University of Virginia in Charlottesville, presented the findings here at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Smart Phone Not for Final Diagnosis
Choudhri tells WebMD that a detailed image can be sent in one to five minutes on a smart phone depending on the type of connection that's being used.
Joseph Tashjian, MD, president of St. Paul Radiology and a spokesman for RSNA, says that the application might also be useful for patients who want to bring their medical records along when visiting another facility.
But the application, which is not approved by the FDA, should not be used to make a final diagnosis, he tells WebMD.
"It's a distribution method that can facilitate decision-making," Tashjian says.
"Transmitting the images over a mobile device allows for instant consultation and diagnosis from a remote location. It can also aid in surgical planning," he says.
What Is Esophageal Cancer? What Is Cancer Of The Esophagus?

Esophageal cancer occurs in the esophagus which is a long hollow tube that runs from the throat to the stomach. The esophagus carries the food that is swallowed all the way to the stomach to be digested. Esophageal cancer usually begins in the cells that line the inside of the esophagus. Cancer happens when some of the cells multiply in an abnormal way, causing a growth called a tumor to form. Tumors can be benign (not cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). They can occur in any part of the body where the cells multiply abnormally. Esophageal cancer is not common. In areas of the world, such as Asia and parts of Africa, esophageal cancer is much more common. Men and people over the age of 55 are most commonly affected esophageal cancer.
Types of cancer of the esophagus:
Squamous cell carcinoma forms in the upper part of the esophagus when cells on the inside lining of the esophagus multiply abnormally.
Adenocarcinoma of the esophagus forms in the lower part of the esophagus when cells inside the mucous glands that line the esophagus multiply abnormally. Mucous glands produce a slimy substance to help food slide down the esophagus more easily.
Other rare types Rare forms of esophageal cancer include choriocarcinoma, sarcoma and small cell cancer.
What are the signs and symptoms of cancer of the esophagus?
A symptom is something the patient feels and reports, while a sign is something other people, such as the doctor detect. For example, pain may be a symptom while a rash may be a sign. When cancer of the esophagus first develops, it rarely causes any symptoms. This is because the tumor will initially be very small. It is only when the cancer starts to become larger and more advanced that symptoms start to develop.
Signs and symptoms of esophageal cancer include:
Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), Unintentional weight loss, Vomiting, Hoarseness, Indigestion, Heartburn, Chest, back and neck pain.
What causes cancer of the esophagus? The precise cause of esophageal cancer is still unclear. However, there are several risk factors that can increase the chances of developing this form of cancer.
Alcohol, Smoking, Chronic acid reflux, Barrett's esophagus, Diet, Age, Chemicals and pollutants. Chemicals and pollutants which are known to increase the risk of esophageal cancer.
The stages of esophageal cancer are:
Stage I. Cancer occurs only in the top layer of cells lining the esophagus.
Stage II. At this stage, the cancer has invaded deeper layers of the esophagus lining and may have spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Stage III. The cancer has spread to the deepest layers of the wall of the esophagus and to nearby tissues or lymph nodes.
Stage IV. At this stage, the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Gene increases effectiveness of drugs used to fight cancer and allows reduction in dosage
 Researchers at the University of Granada have found a suicide gene, called 'gene E', which leads to the death of tumour cells derived from breast, lung and colon cancer, and prevents their growth. The importance of this new gene is that its use to fight cancer can reduce the potent drugs that are currently used, so that could mean more effective treatment for cancer. This research was conducted by Ana Rosa Rama Ballesteros, from the Department of Anatomy and Human Embryology at the University of Granada. Its aim was to study the possibility of reducing the dosage of drugs currently administered to cancer patients using combination therapy with suicide gene E. Scientists from the UGR have shown that the bacteriophage phiX174 killer gene called E, can be used to induce death in tumour cells. So far, attempts to use many chemotherapeutic (cytotoxic) agents similar to the E gene have shown severe limitations resulting from their toxicity and their poor affinity with the tumour.The results of this research suggest the possibility of reducing the concentration of chemotherapeutic agents in current use with cancer patients. Thus, in lung cancer cell line A-549, scientists from the UGR achieved a 14% inhibition of tumour growth and reduced by 100 times the dose of Paclitaxel agent when it was combined with gene E. In the case of colon cancer, the results were similar. However, the most relevant fact was found in the breast cancer cell line MCF-7, in which the dose of the chemotherapeutic agent, doxorubicin, was reduced by 100 times, reaching up to a 21% greater inhibition of tumour proliferation when combined with gene E. Currently, researchers from the UGR are in the process of obtaining a patent for gene E.
Researchers at the University of Granada have found a suicide gene, called 'gene E', which leads to the death of tumour cells derived from breast, lung and colon cancer, and prevents their growth. The importance of this new gene is that its use to fight cancer can reduce the potent drugs that are currently used, so that could mean more effective treatment for cancer. This research was conducted by Ana Rosa Rama Ballesteros, from the Department of Anatomy and Human Embryology at the University of Granada. Its aim was to study the possibility of reducing the dosage of drugs currently administered to cancer patients using combination therapy with suicide gene E. Scientists from the UGR have shown that the bacteriophage phiX174 killer gene called E, can be used to induce death in tumour cells. So far, attempts to use many chemotherapeutic (cytotoxic) agents similar to the E gene have shown severe limitations resulting from their toxicity and their poor affinity with the tumour.The results of this research suggest the possibility of reducing the concentration of chemotherapeutic agents in current use with cancer patients. Thus, in lung cancer cell line A-549, scientists from the UGR achieved a 14% inhibition of tumour growth and reduced by 100 times the dose of Paclitaxel agent when it was combined with gene E. In the case of colon cancer, the results were similar. However, the most relevant fact was found in the breast cancer cell line MCF-7, in which the dose of the chemotherapeutic agent, doxorubicin, was reduced by 100 times, reaching up to a 21% greater inhibition of tumour proliferation when combined with gene E. Currently, researchers from the UGR are in the process of obtaining a patent for gene E.
Painless Needles
 Painless needles are one way technology is improving society. Needles are always scaring young children and even adults. Now with the new painless needle pediatricians can give vaccinations pain free. Researchers at Georgia Institute of Technology call theses new needles micro needles. They are made from silicon, metal, glass or biodegradable polymer. Theses needles are 500 times smaller then ordinary hypodermic needles, which are too small to irritate nerve endings. These new needles will consist of 400 embedded micro needles will be glued to a patch that will gently puncture the skin. Now with this new technology society can have pain free shots.
Painless needles are one way technology is improving society. Needles are always scaring young children and even adults. Now with the new painless needle pediatricians can give vaccinations pain free. Researchers at Georgia Institute of Technology call theses new needles micro needles. They are made from silicon, metal, glass or biodegradable polymer. Theses needles are 500 times smaller then ordinary hypodermic needles, which are too small to irritate nerve endings. These new needles will consist of 400 embedded micro needles will be glued to a patch that will gently puncture the skin. Now with this new technology society can have pain free shots.
New Wound Dressing, Full of Antibiotics, Dissolves When Wound Has Healed.
 Despite advances in treatment regimens and the best efforts of nurses and doctors, about 70% of all people with severe burns die from related infections. But a revolutionary new wound dressing developed at Tel Aviv University could cut that number dramatically. Prof. Meital Zilberman of TAU's Department of Biomedical Engineering has developed a new wound dressing based on fibers she engineered -- fibers that can be loaded with drugs like antibiotics to speed up the healing process, and then dissolve when they've done their job.
Despite advances in treatment regimens and the best efforts of nurses and doctors, about 70% of all people with severe burns die from related infections. But a revolutionary new wound dressing developed at Tel Aviv University could cut that number dramatically. Prof. Meital Zilberman of TAU's Department of Biomedical Engineering has developed a new wound dressing based on fibers she engineered -- fibers that can be loaded with drugs like antibiotics to speed up the healing process, and then dissolve when they've done their job.
Swine Flu Poll: Problems With Vaccine Supply and Safety Concerns
 Nearly half of parents now don't intend to have their children vaccinated against the swine flu virus – and among those who do plan to get the vaccine, more than half say they've been deterred by supply problems, poll finds.
Nearly half of parents now don't intend to have their children vaccinated against the swine flu virus – and among those who do plan to get the vaccine, more than half say they've been deterred by supply problems, poll finds.Nearly half of parents don't plan to vaccinate their kids against the virus. Others, meanwhile, continue to steer clear as a result of undiminished skepticism about the safety of the vaccine itself. Despite federal reassurances, a third of Americans say they're not confident it's safe, much like the 30 percent who said so last month. And 66 percent of adults say they themselves don't plan to get vaccinated - slightly up from 62 percent last month.
Heart attack patients receive radiation equivalent of 725 chest X-rays
 Heart attack patients are exposed to a radiation dose equal to about 725 chest X-rays over the course of their hospital stay, according to research presented Monday at the American Heart Association meeting in Orlando, Florida.
Heart attack patients are exposed to a radiation dose equal to about 725 chest X-rays over the course of their hospital stay, according to research presented Monday at the American Heart Association meeting in Orlando, Florida.The radiation comes from tests such as computed tomography (CT) scans, cardiac catheterizations, and artery-clearing angioplasties.
Too much radiation can increase the risk of developing some cancers, although the benefits of such tests typically outweigh the risks when it comes to diagnosing and treating heart attacks. The cancer risk associated with an angioplasty or with a CT scan -- which delivers about 500 times more radiation than an X-ray -- is hard to measure.
Patients shouldn't be afraid to ask their doctor if a test is truly necessary. "There's nothing wrong with patients asking their doctor, 'How will this test change what you do for me?' If it doesn't, that test may not be necessary."
Routine Mammograms Should Start At 50 Not 40 Says US Expert Panel

An independent medical expert panel that advises the US federal government on preventive and primary healthcare recommends against routine screening mammography in women aged 40 to 49 years and suggests instead that the decision to start regular screening before the age of 50 should be an individual one.The recommendation, dated November 2009, comes from the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF), a leading independent panel of private-sector experts in prevention and primary care, sponsored by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) which is part of the US Department of Health and Human Services. The full statement with supporting documents is available on the AHRQ website.
The USPSTF recommends against routine screening mammography for women under the age of 50 and that for women younger than this the decision to have mammograms every two years should be an individual one that takes into account the patient's individual context, including "the patient's values regarding specific benefits and harms".
The main reason for raising the age band from 40 to 50 comes from a new systematic review that incorporates a randomized controlled trial that showed the risk reduction from screening is greater for women aged 50 to 59 than for those aged 40 to 49. The USPSTF said that the trial estimated that the "number needed to invite for screening to extend one woman's life as 1904 for women aged 40 to 49 years and 1339 for women aged 50 to 59 years", and although the relative risk reduction is nearly the same for the two age groups, risk for breast cancer rises steeply from age 40 onwards, thus the absolute risk reduction from screening as shown by the number that would have to be invited, is greater for those aged 50 to 59 than for women aged 40 to 49.In their new Screening for Breast Cancer statement the USPSTF also recommends:
Regular biennial screening mammography for women aged 50 to 74. Only 40 percent of the lives saved by mammographic screening are of women aged 40 - 49.
Regular biennial screening mammography for women aged 50 to 74. Only 40 percent of the lives saved by mammographic screening are of women aged 40 - 49.
LFCHD hosting two H1N1 vaccination clinics Nov. 7

After providing more than 1,600 H1N1 shots last Saturday to kids with chronic health conditions, the Lexington-Fayette County Health Department is now turning its attention to the remaining target groups.
LFCHD will host H1N1 vaccination clinics 9 a.m.-3 p.m. (or until the vaccine runs out) Saturday, Nov. 7, at Paul Laurence Dunbar High School, 1600 Man O’ War Blvd., and Bryan Station High School, 201 Eastin Road. The shots will be free.
The clinics will target high-risk priority groups identified by the CDC:
• pregnant women
• people between the ages of 6 months through 24 years
• people who live with or care for children younger than 6 months of age
• people ages 25-64 with chronic health disorders or compromised immune systems
• health care and emergency services personnel.
Anyone with a fever Saturday or with egg allergies cannot get the shot.
Additional clinics in November will also target the priority groups, while those who live or work in Fayette County will be focused on during December clinics. The clinics will be held based on availability of the vaccine and could be rescheduled or postponed if there are any delays on the vaccine’s shipment. The health department will post the latest updated information on the clinics on its Flu Hotline, 288-7529, and online at www.LexFluCrew.com.
All H1N1 shots provided by the Lexington-Fayette County Health Department will be free.
For additional information, become a fan of the Lexington-Fayette County Health Department on Facebook, or follow us on Twitter at twitter.com/LFCHD.
Go Red For Women Heart Health Symposium & Luncheon is Nov. 6

Saint Joseph Health System is Central Kentucky Goes Red sponsor
When the American Heart Association presented the Go Red For Women Symposium and Luncheon last year, Central Kentuckians packed the room.
The matter at hand, women’s cardiovascular health, clearly had touched a nerve, and attendees wanted to learn more about heart disease and stroke, women’s perhaps surprisingly high risk, and what could be done about it. They came to the right place.
And they will again in 2009. This year’s Go Red For Women Heart Health Symposium & Luncheon, set for Friday, November 6 at Griffin Gate Marriott Resort & Spa, will offer breakout sessions, a lively keynote speaker, survivor stories and a top-of-the-line luncheon. Registration opens at 9 a.m., breakout sessions start at 9:30 and the luncheon begins at 11:30.
Go Red For Women is an American Heart Association movement to educate women about heart disease. Long thought to be a man’s concern, it is also a woman’s health risk and, in fact, it’s women’s top health threat. It is the No. 1 killer of women and men alike—and actually kills more women than men.
One reason this has been misunderstood is that women’s heart disease warning signs may be different from the well-publicized crushing chest pain that men report, although women also could experience that, too. But other warning signs might be pain in the back, neck, jaw or stomach; shortness of breath; and nausea, cold sweat or lightheadedness. These are alarms to call 9-1-1 immediately.
This message—learn, and act fast if you suspect something is wrong—is a central focus of the Go Red For Women Heart Health Symposium & Luncheon. But that’s only one facet of this diamond. The event’s breakout sessions are State-of-the-Heart Fitness for Women, with James “Eddie” Phipps of Saint Joseph Cardiac Rehabilitation; “Heart Disease” – One Hidden Diagnosis and Its Effect on Women, with Mubashir Qazi, M.D., FACC, FSCAI; and The “Unami” Factor – The Latest in Heart Healthy Cooking, with Whitney Brown, director of consumer affairs for the Kentucky Beef Council.
Then the luncheon shifts into high gear, with a great meal, the Macy’s fashion show featuring cardiovascular disease survivors telling their stories, and guest speaker Eliz Greene, whose program is titled, “The Busy Woman’s Guide to a Healthy Heart.”
The Go Red For Women Heart Health Symposium & Luncheon benefits the American Heart Association, which funds education, advocacy and research—including more than $3.5 million in active awards at UK—to fight heart disease and stroke.
Those who want to attend the event may purchase tables of 10 for $500 each, or individual tickets for $50. For more information or to secure seats, call (859) 278-1632.
2 Days for the BLUEGRASS GREENEXPO! Help us Build a World-Class Green Community!
WHAT: The largest collection of Green Products, Exhibits & Resources ever assembled in Kentucky!
WHEN: October 24-25, 2009, Saturday 10-6 & Sunday 12-6
WHERE: Heritage Hall at Lexington Center
ADMISSION: FREE & Open to the Public
CONTACT: Ben Perry - (859) 523-4773, ben@bluegrassgreenworks.org
WEBSITE: Visit www.bluegrassgreenworks.org
Contact us about becoming a Sponsor, Exhibitor, Educator or Volunteer!
Explore over 40,000 square feet of attractions including a Trade Show, Workshops, Green Building Tours and The Kids Expo, plus Local Art, Entertainment and Food Sampling. New for 2009 is the SUN SPACE, with cooking demos by Great Local Chefs using Fresh Local Foods and Local Artists making and selling their work. Improved for 2009 is an expanded Sustainability Street exhibition on West Main Street, and several new workshops including Green Burials, Wind Energy and more.
See you at the Expo!
Ben B. Perry
President - Bluegrass Greenworks, Inc
PO Box 22580
Lexington, KY 40522-2580
(859) 523-4773 office phone/fax
(859) 327-0924 cell
ben@bluegrassgreenworks.org
www.bluegrassgreenworks.org
WHEN: October 24-25, 2009, Saturday 10-6 & Sunday 12-6
WHERE: Heritage Hall at Lexington Center
ADMISSION: FREE & Open to the Public
CONTACT: Ben Perry - (859) 523-4773, ben@bluegrassgreenworks.org
WEBSITE: Visit www.bluegrassgreenworks.org
Contact us about becoming a Sponsor, Exhibitor, Educator or Volunteer!
Explore over 40,000 square feet of attractions including a Trade Show, Workshops, Green Building Tours and The Kids Expo, plus Local Art, Entertainment and Food Sampling. New for 2009 is the SUN SPACE, with cooking demos by Great Local Chefs using Fresh Local Foods and Local Artists making and selling their work. Improved for 2009 is an expanded Sustainability Street exhibition on West Main Street, and several new workshops including Green Burials, Wind Energy and more.
See you at the Expo!
Ben B. Perry
President - Bluegrass Greenworks, Inc
PO Box 22580
Lexington, KY 40522-2580
(859) 523-4773 office phone/fax
(859) 327-0924 cell
ben@bluegrassgreenworks.org
www.bluegrassgreenworks.org
COMPREHENSIVE MEDICAID SMOKING CESSATION PROGRAM WOULD SAVES LIVES AND TAXPAYER DOLLARS
Advocates for a Medicaid smoking cessation program gathered in Frankfort today to urge Governor Beshear and the General Assembly to fund the $1.5 million needed to implement the comprehensive program created by HB 337 in 2007.
HB 337 created a comprehensive smoking cessation program, including counseling and medications, for the 285,000 smokers on Kentucky Medicaid. Unfortunately, no funding was attached and the program has languished unfunded for more than two years. This leaves Kentucky as one of only six states not to offer such a program.
“This is one of the best moves we could make to keep Kentuckians healthy, prevent life-threatening diseases and hold down health care costs,” said Rep. John Will Stacy, D-West Liberty, who sponsored HB 337 in 2007. “We should be following the advice of virtually all health care experts and embracing treatments with proven track records of helping people who want to give up smoking.”
Kentucky has one of the highest adult smoking rates and the highest smoking-related death rate in the country. Yet, for approximately $5 million ($1.5 from Kentucky and $3.5 in Federal matching funds), the Commonwealth could save thousands of lives and reduce our state’s Medicaid costs by millions per year.
“The framework is in place for a comprehensive program for Medicaid patients and all we have to do is fund it,” said Dr. Jon White, President of the Kentucky Medical Association. “This is sound public health policy that makes fiscal sense.”
A similar program has already proven successful in Kentucky through Passport Health Plan which provides smoking cessation benefits to its Medicaid recipients in the Louisville-area. Since 2007, more than one thousand people have enrolled in Passport’s cessation program and 51% have successfully quit smoking. Unfortunately, this same affordable opportunity to quit smoking and live healthier is not offered to the rest of Kentucky’s Medicaid recipients.
For just $1.5 million we can end the health disparity for the rest of Kentucky’s Medicaid recipients, help thousands of Kentuckians quit smoking, and save millions of taxpayer dollars in the process.
Media Contact:
Steve Bryant
502.296.1863
sbryant@perituspr.com
HB 337 created a comprehensive smoking cessation program, including counseling and medications, for the 285,000 smokers on Kentucky Medicaid. Unfortunately, no funding was attached and the program has languished unfunded for more than two years. This leaves Kentucky as one of only six states not to offer such a program.
“This is one of the best moves we could make to keep Kentuckians healthy, prevent life-threatening diseases and hold down health care costs,” said Rep. John Will Stacy, D-West Liberty, who sponsored HB 337 in 2007. “We should be following the advice of virtually all health care experts and embracing treatments with proven track records of helping people who want to give up smoking.”
Kentucky has one of the highest adult smoking rates and the highest smoking-related death rate in the country. Yet, for approximately $5 million ($1.5 from Kentucky and $3.5 in Federal matching funds), the Commonwealth could save thousands of lives and reduce our state’s Medicaid costs by millions per year.
“The framework is in place for a comprehensive program for Medicaid patients and all we have to do is fund it,” said Dr. Jon White, President of the Kentucky Medical Association. “This is sound public health policy that makes fiscal sense.”
A similar program has already proven successful in Kentucky through Passport Health Plan which provides smoking cessation benefits to its Medicaid recipients in the Louisville-area. Since 2007, more than one thousand people have enrolled in Passport’s cessation program and 51% have successfully quit smoking. Unfortunately, this same affordable opportunity to quit smoking and live healthier is not offered to the rest of Kentucky’s Medicaid recipients.
For just $1.5 million we can end the health disparity for the rest of Kentucky’s Medicaid recipients, help thousands of Kentuckians quit smoking, and save millions of taxpayer dollars in the process.
Media Contact:
Steve Bryant
502.296.1863
sbryant@perituspr.com
Health department launches special flu website
To help provide the most updated information about the flu, including H1N1, the Lexington-Fayette County Health Department has launched a special website, www.LexFluCrew.com.
“The people of Lexington have several questions about the flu this fall, and we are using LexFluCrew.com to provide answers and calm any fears,” said Kevin Hall, LFCHD spokesman. “Along with our Facebook and Twitter accounts and our Flu Hotline, the Lexington-Fayette County Health Department is reaching people in new and exciting ways.”
The LexFluCrew.com site will be used to provide information on vaccination clinics, volunteer opportunities and more, as well as answer frequently asked questions.
“We’re excited about offering this service to Lexington residents and look forward to continuing our educational efforts about the flu,” Hall said.
For additional information, become a fan of the Lexington-Fayette County Health Department on Facebook, or follow us on Twitter at twitter.com/LFCHD. The Flu Hotline can be reached at 288-7529.
“The people of Lexington have several questions about the flu this fall, and we are using LexFluCrew.com to provide answers and calm any fears,” said Kevin Hall, LFCHD spokesman. “Along with our Facebook and Twitter accounts and our Flu Hotline, the Lexington-Fayette County Health Department is reaching people in new and exciting ways.”
The LexFluCrew.com site will be used to provide information on vaccination clinics, volunteer opportunities and more, as well as answer frequently asked questions.
“We’re excited about offering this service to Lexington residents and look forward to continuing our educational efforts about the flu,” Hall said.
For additional information, become a fan of the Lexington-Fayette County Health Department on Facebook, or follow us on Twitter at twitter.com/LFCHD. The Flu Hotline can be reached at 288-7529.
Health department schedules H1N1 vaccine clinics for public
Lexington residents wishing to fight the flu this fall will get their first shot at the H1N1 vaccine through a series of weekend clinics hosted by the Lexington-Fayette County Health Department starting Saturday, Nov. 7.
The clinics will target the priority groups identified by the CDC: pregnant women, people between the ages of 6 months through 24 years, people who live with or care for children younger than 6 months of age, people ages 25-64 with chronic health disorders or compromised immune systems and health care and emergency services personnel.
The clinics will be held based on availability of the vaccine and could be rescheduled or postponed if there are any delays on the vaccine’s shipment. The health department will post the latest updated information on the clinics on its Flu Hotline, 288-7529, and online at www.LexFluCrew.com.
The H1N1 vaccine clinic schedule is:
• 9 a.m.-3 p.m. Nov. 7
o Paul Laurence Dunbar High School, 1600 Man O’ War Blvd.
o Bryan Station High School, 201 Eastin Road
• 9 a.m.-3 p.m. Nov. 21
o Tates Creek Middle School, 1105 Centre Parkway
o Jessie Clark Middle School, 3341 Clays Mill Road
• 9 a.m.-3 p.m. Dec. 5
o Henry Clay High School, 2100 Fontaine Road
o Bryan Station High School, 201 Eastin Road
• 1-5 p.m. Dec. 6
o Henry Clay High School, 2100 Fontaine Road
o Bryan Station High School, 201 Eastin Road
• 9 a.m.-3 p.m., Dec. 12
o Beaumont Middle School, 2080 Georgian Way
o Lexington Traditional Magnet, 350 N. Limestone
• 9 a.m.-3 p.m. Dec. 19
o Paul Laurence Dunbar High School, 1600 Man O’ War Blvd.
o Tates Creek High School, 1111 Centre Parkway
LFCHD will also be hosting a large-scale drive-thru clinic 10 a.m.-3 p.m. Nov. 14 in the parking lot at Lexmark.
All H1N1 shots provided by the Lexington-Fayette County Health Department will be free.
For additional information, become a fan of the Lexington-Fayette County Health Department on Facebook, or follow us on Twitter at twitter.com/LFCHD.
The clinics will target the priority groups identified by the CDC: pregnant women, people between the ages of 6 months through 24 years, people who live with or care for children younger than 6 months of age, people ages 25-64 with chronic health disorders or compromised immune systems and health care and emergency services personnel.
The clinics will be held based on availability of the vaccine and could be rescheduled or postponed if there are any delays on the vaccine’s shipment. The health department will post the latest updated information on the clinics on its Flu Hotline, 288-7529, and online at www.LexFluCrew.com.
The H1N1 vaccine clinic schedule is:
• 9 a.m.-3 p.m. Nov. 7
o Paul Laurence Dunbar High School, 1600 Man O’ War Blvd.
o Bryan Station High School, 201 Eastin Road
• 9 a.m.-3 p.m. Nov. 21
o Tates Creek Middle School, 1105 Centre Parkway
o Jessie Clark Middle School, 3341 Clays Mill Road
• 9 a.m.-3 p.m. Dec. 5
o Henry Clay High School, 2100 Fontaine Road
o Bryan Station High School, 201 Eastin Road
• 1-5 p.m. Dec. 6
o Henry Clay High School, 2100 Fontaine Road
o Bryan Station High School, 201 Eastin Road
• 9 a.m.-3 p.m., Dec. 12
o Beaumont Middle School, 2080 Georgian Way
o Lexington Traditional Magnet, 350 N. Limestone
• 9 a.m.-3 p.m. Dec. 19
o Paul Laurence Dunbar High School, 1600 Man O’ War Blvd.
o Tates Creek High School, 1111 Centre Parkway
LFCHD will also be hosting a large-scale drive-thru clinic 10 a.m.-3 p.m. Nov. 14 in the parking lot at Lexmark.
All H1N1 shots provided by the Lexington-Fayette County Health Department will be free.
For additional information, become a fan of the Lexington-Fayette County Health Department on Facebook, or follow us on Twitter at twitter.com/LFCHD.
Protecting yourself from the dreaded "swine flu"

No worries about keeping the "B" on your BLT sandwich. The H1N1 influenza virus, the "swine flu" that caused hundreds of deaths around the world earlier this year, is not caused by eating pigs.
The flu virus is spread through sneezing, coughing and contact with infected individuals. The virus infects not only humans, but also pigs, birds, horses and, rarely, dogs. Sometimes, a virus can "leap" from one species to another.
The flu virus is spread through sneezing, coughing and contact with infected individuals. The virus infects not only humans, but also pigs, birds, horses and, rarely, dogs. Sometimes, a virus can "leap" from one species to another.
When this happens, a new virus can sometimes emerge from an infected human or animal," said Dr. Chris Nelson, associate professor in the University of Kentucky College of Medicine and chief of its Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases.
Symptoms of the H1N1 flu virus in people include fever, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, body aches, headache, chills and fatigue. About one in four of those infected also reported diarrhea and vomiting.
New vaccines to protect against H1N1 are now being tested for use this fall. To ensure full protection, Nelson says, the vaccine will probably be given in two parts, a starter dose followed by a booster about 30 days later.
However, in the event of a vaccine shortage, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has established a vaccination priority list of those most at risk for serious complications from influenza. It can be viewed on the CDC Web site at www.cdc.gov/h1n1flu
However, in the event of a vaccine shortage, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has established a vaccination priority list of those most at risk for serious complications from influenza. It can be viewed on the CDC Web site at www.cdc.gov/h1n1flu
The CDC advises the following precautions:
· Cover your nose and mouth with a tissue when you cough or sneeze. Throw the tissue in the trash after you use it.
· Wash your hands often with soap and water, especially after you cough or sneeze. Alcohol-based hand cleaners are also effective.
· Avoid touching your eyes, nose or mouth. Germs spread this way.
· Try to avoid close contact with sick people.
· If you are sick with flu-like illness, stay home for at least 24 hours after your fever is gone except to get medical care or for other necessities. (Your fever should be gone without the use of a fever-reducing medicine.) Keep away from others as much as possible to keep from making others sick.
· Cover your nose and mouth with a tissue when you cough or sneeze. Throw the tissue in the trash after you use it.
· Wash your hands often with soap and water, especially after you cough or sneeze. Alcohol-based hand cleaners are also effective.
· Avoid touching your eyes, nose or mouth. Germs spread this way.
· Try to avoid close contact with sick people.
· If you are sick with flu-like illness, stay home for at least 24 hours after your fever is gone except to get medical care or for other necessities. (Your fever should be gone without the use of a fever-reducing medicine.) Keep away from others as much as possible to keep from making others sick.
Another way to protect your health is to stay informed by visiting the following Web sites, which are frequently updated as the situation changes:
· CDC: www.cdc.gov/h1n1flu
· Kentucky Health Alerts: http://healthalerts..ky.gov
· WHO: www.who.int/csr/disease/swineflu
· CDC: www.cdc.gov/h1n1flu
· Kentucky Health Alerts: http://healthalerts..ky.gov
· WHO: www.who.int/csr/disease/swineflu
Osteoarthritis Pain
 Osteoarthritis (OA) is common, affecting 27 million people in the United States, and accounts for 25 percent of physician office visits. By age 65, 80 percent of the U.S. population will have x-ray evidence of OA; however, only two-thirds will have symptoms. Over the last decade, hospitalizations related to OA have doubled. It is the leading chronic disability in the US. Therefore this is a serious and important clinical problem.
Osteoarthritis (OA) is common, affecting 27 million people in the United States, and accounts for 25 percent of physician office visits. By age 65, 80 percent of the U.S. population will have x-ray evidence of OA; however, only two-thirds will have symptoms. Over the last decade, hospitalizations related to OA have doubled. It is the leading chronic disability in the US. Therefore this is a serious and important clinical problem.The cause of OA is not clear. Trauma can cause OA but genetics, lifestyle and metabolism play a role. The knees, hands, hips and back are frequently affected.
Cartilage lubricates joints and helps to absorb stress. As we age, we lose joint cartilage and underlying bone may be damaged. This may cause increasing pain. As train increases, patients may be fearful of joint movement, which may cause muscle damage.
OA patients have use-related pain, stiffness, reduced movement and feelings of unstable joints. They experience joint tender spots, swelling, cracking noises of the joint, locking up of the joint and signs of mild inflammation. Excessive warmth, redness and swelling should cause the patient to see their physician.
Currently, we do not have a treatment that reverses OA damage; treatment is symptomatic. Joints can be injected with a thick material that mimics the fluid in a joint. Patients can receive medications for their pain, and physical therapy can help with the reduction in function. The approach needs to be multidisciplinary.
At the Pain Treatment Center of the Bluegrass, we are engaged in the treatment of OA as well as clinical research in OA. John F. Peppin, D.O., F.A.C.P., Director Clinical Research Division
The Pain Treatment Center of the BluegrassClinical Associate Professor, University of Kentucky, Associate Medical Director, Hospice of the Bluegrass
2416 Regency Road
Lexington, Kentucky 40503
859 278-1316 ext. 266859 260-2467
859 276-3847 FAX
Ten Questions you should ask your Pharmacist
 Take a look at the prescription medications you have in your cabinet. Now, without cheating, could you tell somebody one of the side effects you may need to watch out for while taking them? How about telling them what you would do if you forgot a dose? These are only some of the things that every person should know about their medications, yet many walk out of the pharmacy with new prescriptions barely remembering the name of the medicine. Here are 10 questions you should ask your pharmacist before taking a new medication:
Take a look at the prescription medications you have in your cabinet. Now, without cheating, could you tell somebody one of the side effects you may need to watch out for while taking them? How about telling them what you would do if you forgot a dose? These are only some of the things that every person should know about their medications, yet many walk out of the pharmacy with new prescriptions barely remembering the name of the medicine. Here are 10 questions you should ask your pharmacist before taking a new medication:1. What is the name of the medication, what is its strength, and what is it used for?
2. When and how should I take my medication?
3. How long should I take it?
4. Will this interact with any of my other medications, over-the-counter products or supplements?
5. Should I avoid alcohol, other medications, certain foods, or certain activities while I am on this medication?
6. Should I expect any side effects?
7. Is it possible to develop an allergic reaction to this medication?
8. What should I do if I forget to take my medication?
9. How should I store my medication?
10. Is there a generic version of this medication available?
To know in detail about the question, visit our site at http://healthandwellnessmagazine.net/index.php
(or) Read our Health&Wellness Magazine.
Regular Check-Ups are Important
 It's time to take charge of your health! Take advantage of low and or no costs screenings in your community or schedule an appointment with your health care provider to discuss what preventive health services you need and when you need them.
It's time to take charge of your health! Take advantage of low and or no costs screenings in your community or schedule an appointment with your health care provider to discuss what preventive health services you need and when you need them.Many medical conditions and or diseases are preventable and or treatable and beatable! Regular health exams and tests can help find problems before they start.
The CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) recommends the following routine screenings:
- Breast and Cervical Cancer Early
- Detection
- Cholesterol
- Colorectal Cancer Screening
- Diabetes
- High Blood Pressure
- Immunization
- Oral Health for Adults
- Prostate Cancer Screening
- Skin Cancer
Free Prostate Screening – September 16th and December 2nd University of KY Markey Cancer Center Call 257-4488 for appointments
Obesity Linked to Vitamin D Deficiency
 With sweet scents of spring in the air and the breaking sunlight alluring us outside, vitamin D deficiency is the last thing on our minds. Besides, it shouldn’t be an issue since we’re all walking more outside now to shed that winter weight. Right? Actually, vitamin D deficiency might be one of the many reasons why those pounds have seemed so stubborn.
With sweet scents of spring in the air and the breaking sunlight alluring us outside, vitamin D deficiency is the last thing on our minds. Besides, it shouldn’t be an issue since we’re all walking more outside now to shed that winter weight. Right? Actually, vitamin D deficiency might be one of the many reasons why those pounds have seemed so stubborn.The field of bariatric (weight loss) medicine is constantly blooming with new scientific findings. Bariatricians already know there are hundreds of reasons why someone might be struggling with their weight loss, but recently, vitamin D deficiency is being investigated as another biochemical weight-related concern. Since it’s the most common vitamin deficiency and prevalence is on the rise, it should be a big concern to us all. Now physicians also know that vitamin D deficiency is linked to obesity.
Other symptoms associated with vitamin D deficiency: depression, mood swings, forgetfulness, fatigue, weakened immunity, muscle weakness, aches and pains, bone fractures, sleep irregularities, and interference with weight loss.
Things That Decrease Vitamin D Levels:- Clothing- Window Glass (you don't generate vitamin D when sitting in your car or home) - Clouds/Shade- Sunscreen ≥ SPF 8 - Higher Latitude States (UV waves are often not strong enough to make vitamin D from September through May)- Dark Skin (needs to be exposed to the sun longer to make vitamin D)- Age >65 years (4x decrease in vitamin D conversion)- Malabsorptive & Kidney Problems- Lowered Estrogen Levels (menopause)
What Should You Do? - 10-15 minutes of sun exposure in the summer months (early morning and late afternoon) for light skin. Dark skin may need 40 minutes. Of course, too much sun exposure can lead to skin damage and skin cancers. - Dietary intake: there are only a few natural food sources of vitamin D. Therefore, most Americans receive it through fortified food products such as milk and breakfast cereals. Unfortunately, you’d have to drink 10 glasses of fortified milk daily, (1,000 extra calories) to get to minimum levels of vitamin D. Even the, it would still be in a form less readily available to the body.- Vitamin D supplements: Adequate intake of vitamin D vary based on a person’s age, however, current guidelines put the upper limit in persons with no known deficiencies to 2000 IU daily. - If you are having difficulty managing your weight, getting a vitamin D level is strongly advised. See a medical weight loss specialist (bariatrician) to see if vitamin D deficiency or other metabolic and biochemical issues might be holding back your weight loss efforts.
Medical Bariatrics of Lexington in Hamburg is home to Lexington’s only board certified bariatricians that help patients lose weight non- surgically, feel better, and live a healthier happier life in an affordable way. You can call them at (859) 263-SLIM(7546); or learn more about them at http://www.lexingtonkyweightloss.com/
Go Green and Take Action Against Violence
 Statistics help us put things into perspective. Sometimes statistics can be fun. For instance, take “one in three”. There are some odd facts associated with this ratio.- One in three people illegally download music off the Internet.- One in three Americans is raised as Catholic.- One in three Australians is at risk of developing kidney disease.- Ironically, one in three people actually believe marketing statistics. However, there is one national “one in three” statistic that carries with it grave implications for young women and men. That is the statistic on relationship violence. Today, in high schools and on campuses, one in three young women and men is a victim of one or more of a whole menu of behaviors, including stalking, physical and emotional violence, and rape.
Statistics help us put things into perspective. Sometimes statistics can be fun. For instance, take “one in three”. There are some odd facts associated with this ratio.- One in three people illegally download music off the Internet.- One in three Americans is raised as Catholic.- One in three Australians is at risk of developing kidney disease.- Ironically, one in three people actually believe marketing statistics. However, there is one national “one in three” statistic that carries with it grave implications for young women and men. That is the statistic on relationship violence. Today, in high schools and on campuses, one in three young women and men is a victim of one or more of a whole menu of behaviors, including stalking, physical and emotional violence, and rape.In the Green Dot program, each instance of violence or bystander nonintervention is considered a Red Dot. Green Dots are instances where a bystander takes action against violence. The types of action are defined in the Green Dot Bystanders Pledge, http://www.greendotkentucky.com/.
“A green dot is any behavior‚ choice‚ word or attitude that promotes safety for everyone and communicates utter intolerance for rape, domestic violence and stalking. A green dot is intervening in a high risk situation – a green dot is sponsoring a fundraiser for prevention efforts – a green dot is responding to a victim-blaming statement with words of support – a green dot is hanging a prevention poster in your office or business – a green dot is teaching your kids about respect– a green dot is putting a link on your website to your local prevention program - a green dot is providing safety information on the counter at your business. A green dot is simply your individual choice at any given moment to make our state safer.” The goal is simple: displace red dots with green dots. This is done by tapping into the potential of bystanders, particularly those in a group who are obvious leaders. In the Green Dot program, these leaders are taught to identify and effectively react to high-risk situations. Leaders then go out and share the message that violence is not longer accepted behavior. It brings prevention down to individual acts, thus making a solution within the reach of everyone involved.
The Green Dot Program at the UK grew from 14 participants to more than 1,400 participants in just three years. It has been adopted statewide by the Kentucky Domestic Violence Association (http://www.kdva.org/) and the Kentucky Association of Sexual Assault Programs (http://kyasap.brinkster.net/).
For more imformation about the article visit our site http://healthandwellnessmagazine.net/index.php
(or) Read our Health & Wellness Magazine September issue.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)






